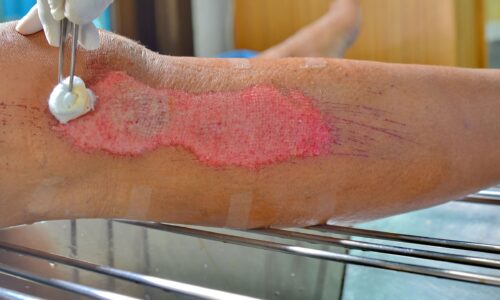
The body heals wounds through a precise biological mechanism, and while skin protects internal tissues, breaks in this barrier require medical attention. Proper wound care supports natural healing, and it may help prevent severe complications. Medical professionals assess the damage depth accurately, and they create a plan based on specific patient needs. Here is more information about the wound healing process:
Infection Control
Because bacteria thrive, preventing infection remains the primary goal. Providers clean the affected area thoroughly to remove contaminants, and they monitor the site closely for signs of redness. When there is heat, it typically indicates a developing issue beneath the surface. Oral antibiotics treat systemic bacterial spread effectively, and controlling this permits the body to focus on repair.
Wound Dressings
Dry gauze covers the wound, but moist dressings are designed to promote faster healing. Modern medicine utilizes various advanced materials for specific injuries. When a wound stays moist, cells regenerate much more efficiently. This environment supports the body’s natural repair systems, and new tissue grows best in hydrated conditions. Changing the dressing prevents fluid buildup around the edges.
Various wound care products manage moisture levels, and they can help prevent tissue breakdown. Excess fluid damages the surrounding healthy skin margins. Depending on the volume of drainage present, a correct moisture balance prevents the wound from drying out.
If infection poses a risk, silver dressings release antimicrobial agents. Collagen products are used to encourage growth, yet they require a clean wound bed. Doctors select appropriate coverings based on changing wound characteristics. The right dressing choice accelerates the overall closure rate. Specialists adjust the protocol as the wound improves, and advanced products actively interact with the wound bed.
Surgery Options
Dead tissue blocks healing, so surgeons perform debridement procedures. Sharp instruments remove necrotic material precisely during office visits. While enzymatic agents work slowly, they dissolve dead tissue effectively. A clean base allows new skin cells to migrate, and biological therapies also help clean the wound bed, which prepares the area for final closure.
Large wounds typically require more advanced skin grafting techniques. Because some defects are deep, flap reconstruction provides the necessary blood supply. The surgeon typically takes skin from elsewhere, and they place it over the wound. This technique covers exposed structures, such as bone or tendon. It provides immediate coverage for large open areas, and successful grafting requires immobilization during the initial phase.
Recovery Period
While the skin closes, the remodeling phase typically continues for months. Nutrition plays a major role in restoring tissue strength. Smoking may constrict blood vessels, and this habit slows recovery significantly. Patients can support their bodies by observing these factors:
- Managing blood sugar levels
- Keeping pressure off the area
- Following protein-rich diets
Adherence to these rules supports the immune system, and comorbidities can complicate the expected timeline.
Schedule Wound Care Services Today
Complicated wounds require expertise, so professional evaluation is necessary. Our team offers comprehensive management plans for stalled injuries. If a wound has not healed recently, seek help immediately. Early intervention prevents amputation in severe cases, and prompt treatment typically reduces the total healing time. Contact a wound care specialist to book your appointment today.